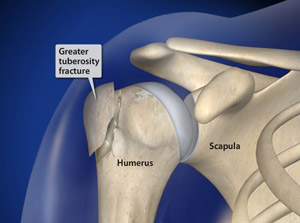
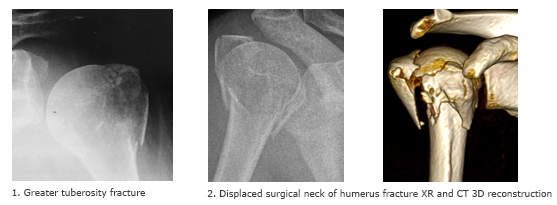
Greater Tuberosity Fracture Treatment
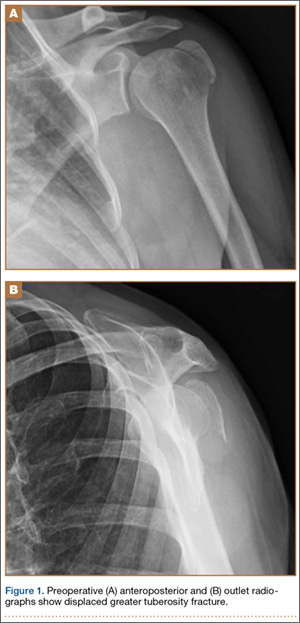
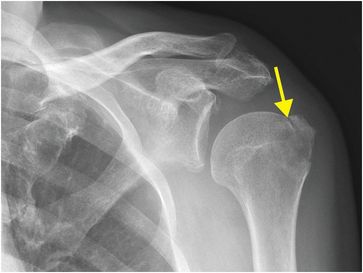
Greater tuberosity fracture treatment. Conservatively treated fracture of the greater tuberosity. Surgical Treatment of Displaced Greater Tuberosity Fractures of the Humerus Abstract Greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus can be successfully treatednonsurgicallyinmostpatientsHoweveraslittleas3to5mm of superior greater tuberosity displacement may adversely affect rotator cuff biomechanics and lead to subacromial impingement in. After the initiation of physical therapy he was diagnosed with an isolated greater tuberosity fracture.
ANSWER Fractures of greater tuberosity can occur in isolation or in combination with anterior dislocation of the shoulder. Stopping smoking during the healing phase of your fracture will. You have sustained an un-displaced fracture to your greater tuberosity of your shoulder.
This normally takes between 6-12 weeks to unite heal. In the first phase patients were immobilized in a sling for 3 weeks. Patients were treated with a three-phase protocol.
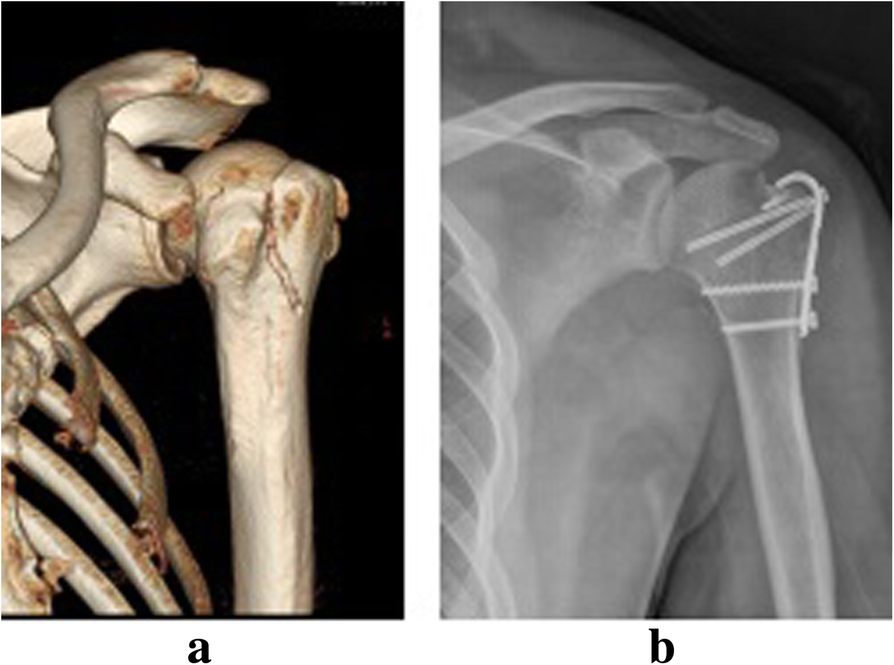
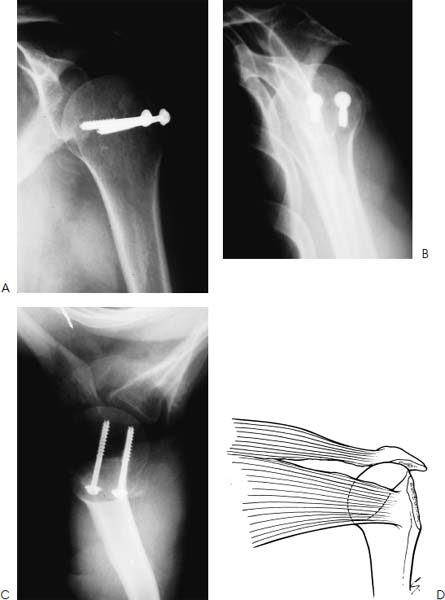
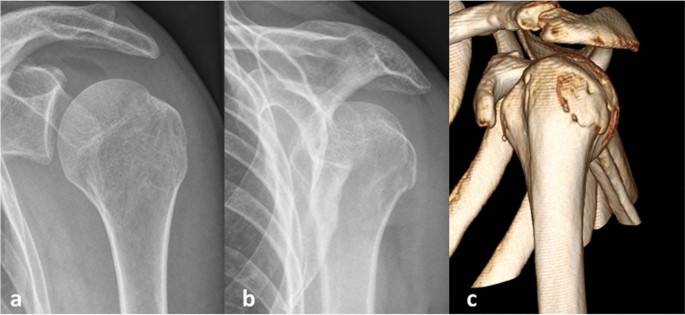
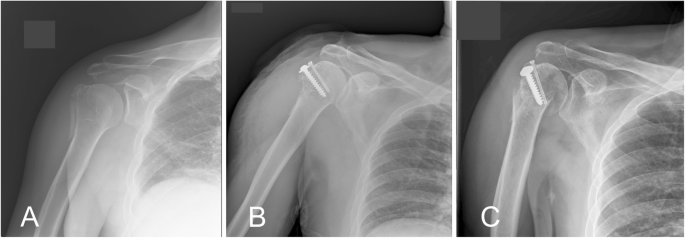
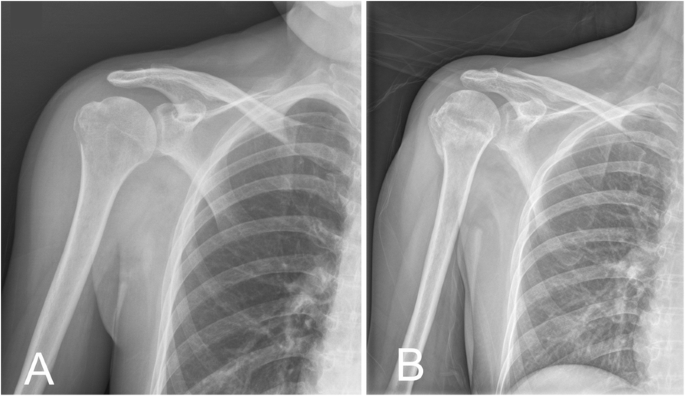
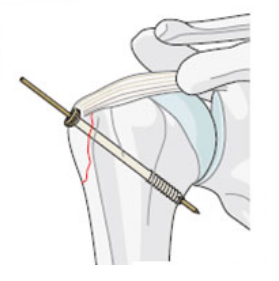
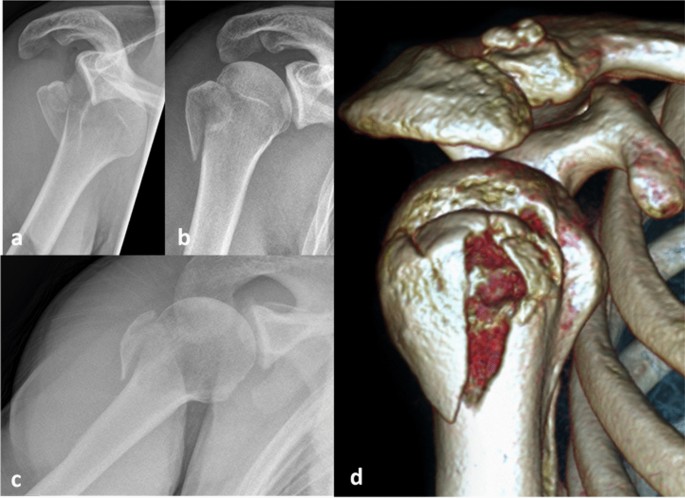
For isolated greater tuberosity fractures include fragment excision open reduction and internal fix-ation ORIF closed reduction with percutaneous fixation and arthroscopically assisted reduction with internal fixation3910 We conducted a study to determine the man-agement patterns for isolated greater tuberosity fractures. While most greater tuberosity fractures can be treated nonoperatively fractures with greater than 5 mm of displacement have been shown to limit abduction decrease external rotation and result in symptomatic subacromial impingement. Initial radiograph a follow-up after 3 weeks to exclude secondary displacement b and anatomic consolidation 3 months after the injury c.
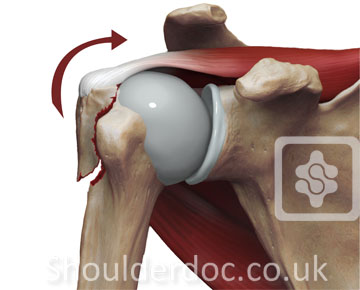
The shoulder is a ball and socket joint you have fractured the outside of the ball part. The patient was a 45-year-old male who sustained a shoulder injury as the result of a fall while skiing. It is during this immobilisation period most of the complication develops and most common of them is joint stiffness and pain.
In these cases surgical treatment is recommended. A cold pack ice pack or frozen peas wrapped in a damp towel can provide short term pain relief. However as little as 3 to 5 mm of superior greater tuberosity displacement may adversely affect rotator cuff biomechanics and lead to subacromial impingement in patients who are active.
Sometimes swelling also develops in forearm and hand. Nearly 80 are undisplaced or only minimal displaced and therefore non-operative treatment is appropriate.
As treatment decisions depend on the size of the fracture and how far it has pulled away from its normal or anatomic location a CT scan is often obtained.
Greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus can be successfully treated nonsurgically in most patients. ANSWER Fractures of greater tuberosity can occur in isolation or in combination with anterior dislocation of the shoulder. In fractures of the greater tuberosity andor the surgical neck the fracture may rest in better reduction if the arm is immobilized in abduction with a cushion. Apply this to the sore area for up to 15 minutes every few hours ensuring the ice is never in direct contact with the skin. It is important that you consider this information with relation to your recent injury. Initial radiograph a follow-up after 3 weeks to exclude secondary displacement b and anatomic consolidation 3 months after the injury c. Surgical Treatment of Displaced Greater Tuberosity Fractures of the Humerus Abstract Greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus can be successfully treatednonsurgicallyinmostpatientsHoweveraslittleas3to5mm of superior greater tuberosity displacement may adversely affect rotator cuff biomechanics and lead to subacromial impingement in. Greater tuberosity fracture rehabilitation After the fracture the shoulder joint is immobilized in sling for roughly one to one and half month. We retrospectively analyzed the records of patients diagnosed with minimally displaced.
Try to rest your shoulder for the first 24-72 hours. In contrast if the boney piece is pulled 5mm away or more surgery is recommended. Initial radiograph a follow-up after 3 weeks to exclude secondary displacement b and anatomic consolidation 3 months after the injury c. We retrospectively analyzed the records of patients diagnosed with minimally displaced. While most greater tuberosity fractures can be treated nonoperatively fractures with greater than 5 mm of displacement have been shown to limit abduction decrease external rotation and result in symptomatic subacromial impingement. Once these goals have been achieved rehabilitative exercises can begin to restore range of motion followed by strength and function. We hypothesized that greater tuberosity fractures displaced.































Posting Komentar untuk "Greater Tuberosity Fracture Treatment"