Which Cells Are Affected In Digeorge Syndrome?
Which cells are affected in digeorge syndrome?. Most people with DiGeorge syndrome are missing a small piece of chromosome 22 known as. 16p112 Deletion Syndrome. DiGeorge Syndrome Prognosis.
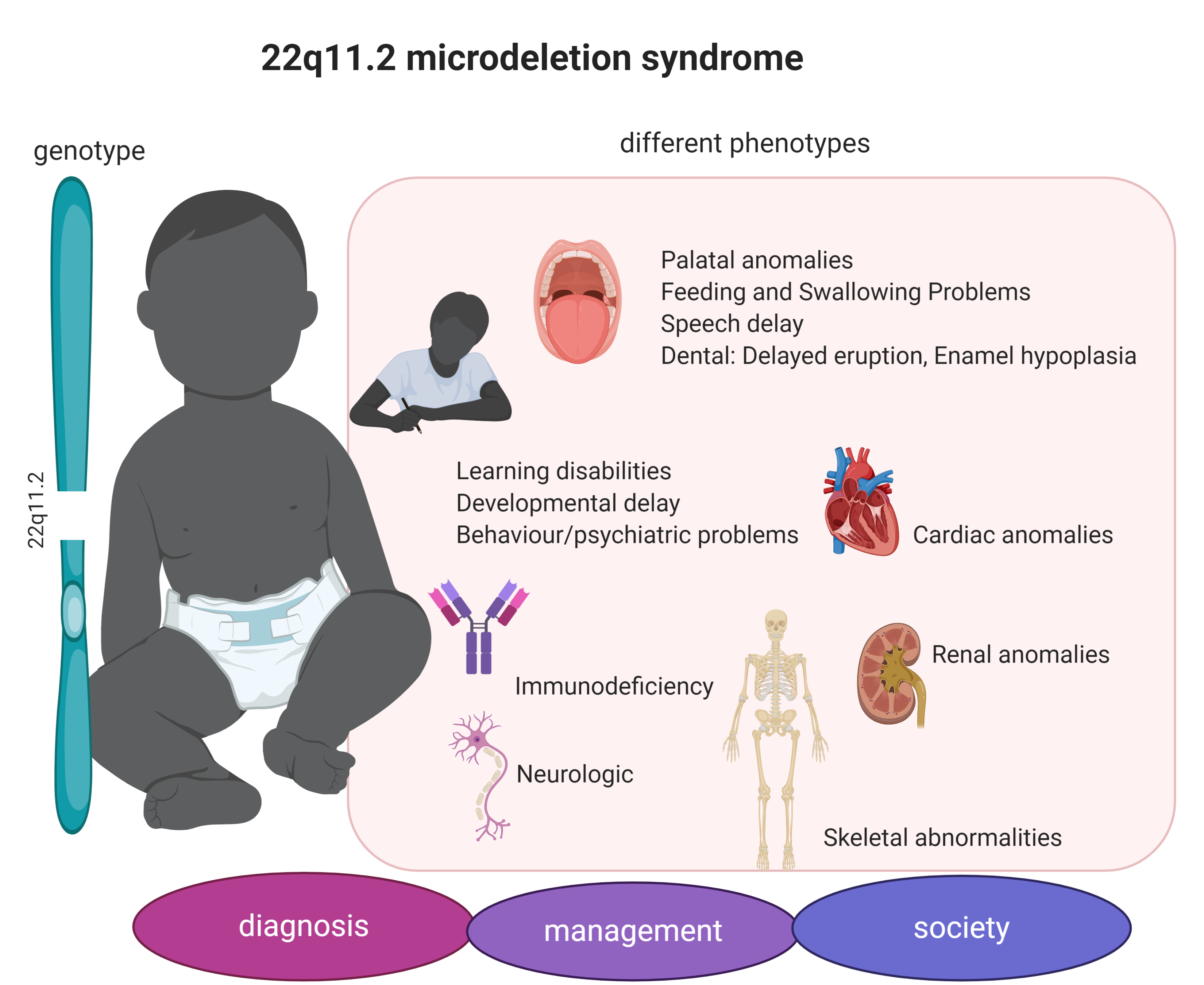
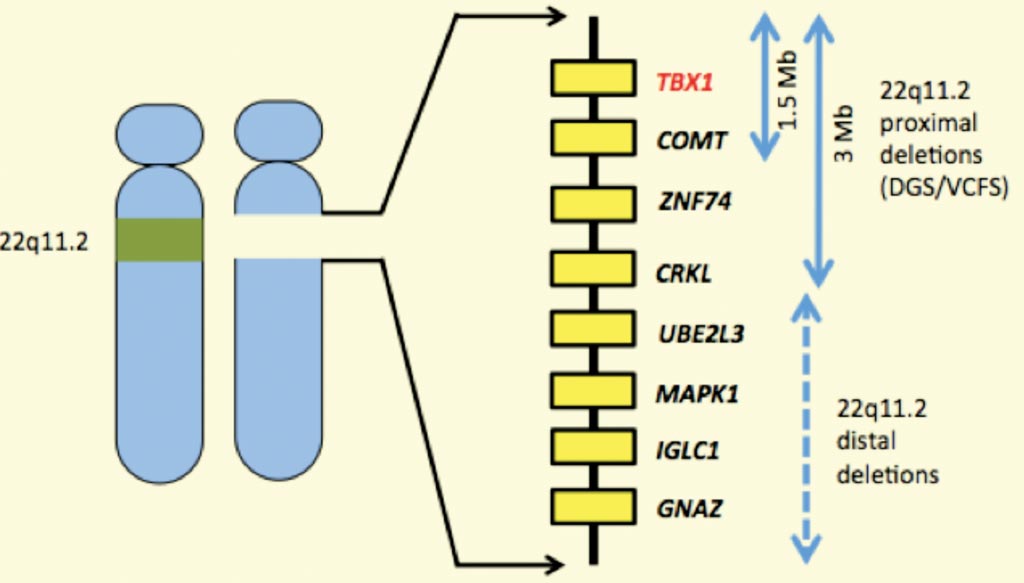
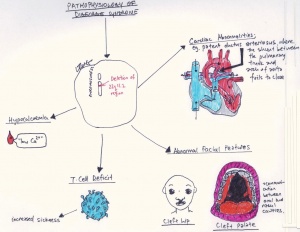
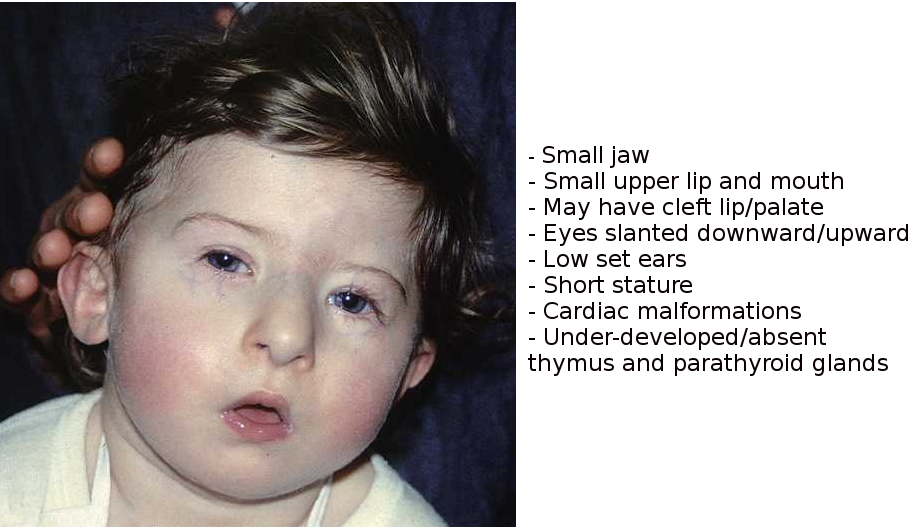
Hypoplasia of the hyoid. While the symptoms can vary they often include congenital heart problems specific facial features frequent infections developmental delay learning problems and cleft palate. Ninety percent of cases of DiGeorge syndrome are caused by a segmental deletion in chromosome 22.
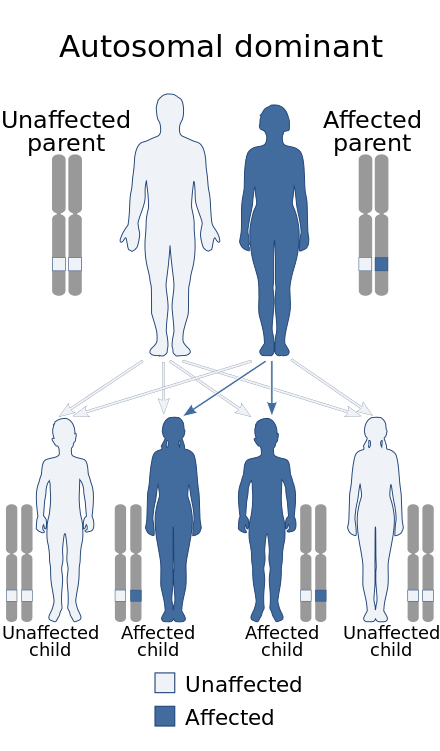
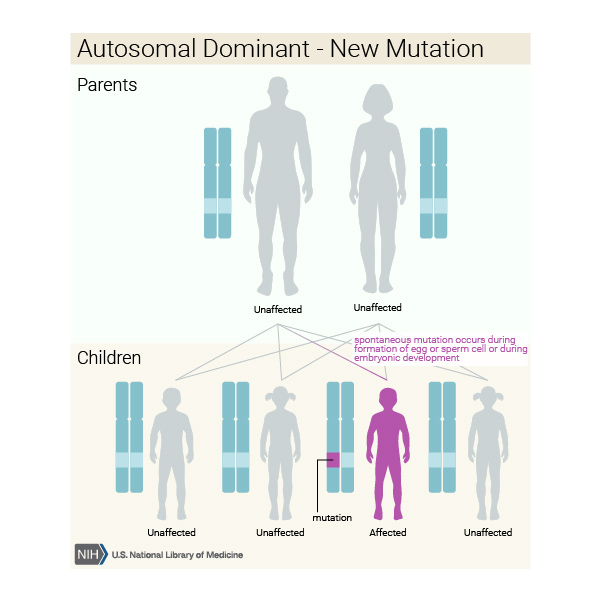
In some cases DiGeorge syndrome 22q112 deletion syndrome may be passed from an affected parent to a child. DiGeorge syndrome is associated with deletions or translocations of a small segment in the human chromosome 22. Associated conditions include kidney problems hearing loss and autoimmune.
If youre concerned about a family history of 22q112 deletion syndrome or if you already have a child with the syndrome you may want to consult a doctor who specializes in genetic disorders geneticist or a genetic counselor for. This deletion may disrupt rostral neural crest cell migration or development. Individuals born with this syndrome often have delayed development.
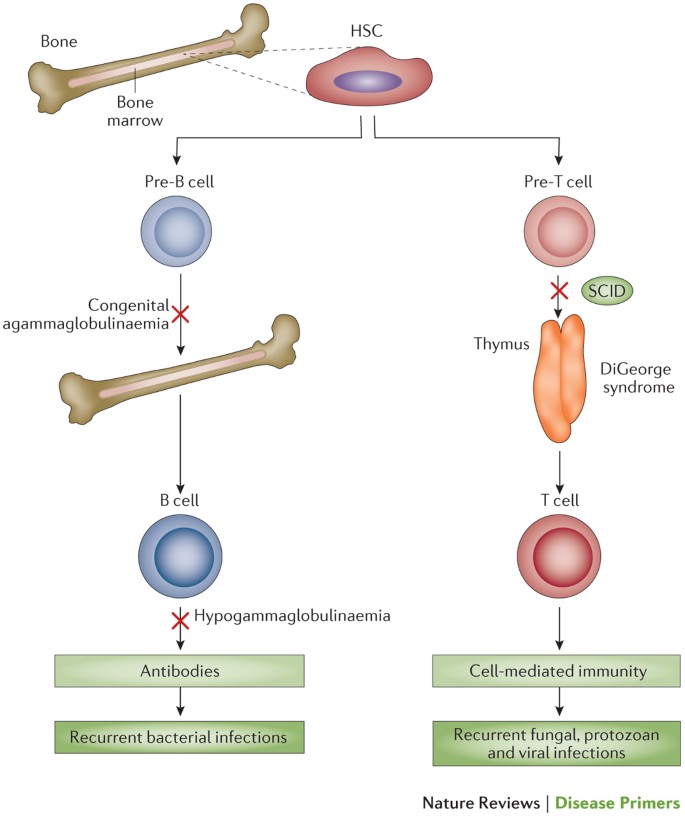
DiGeorge syndrome is a genetic disorder that can affect many parts of the body. What is DiGeorge syndrome. The prognosis for any child with DiGeorge syndrome is variable with many infants dying from devastating seizures infections or failure of the heart within the first year.
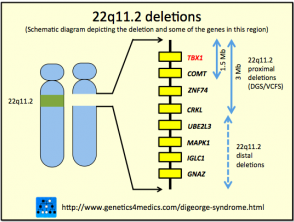
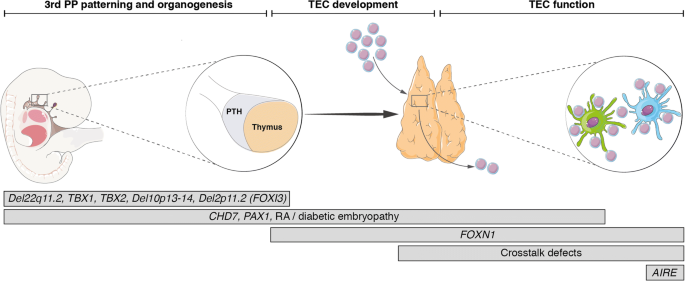
DiGeorge syndrome also known as 22q112 deletion syndrome is a syndrome caused by the deletion of a small segment of chromosome 22. These problems usually present at a babys birth or in early childhood include heart defects an impaired immune system and developmental delays. However the manifestations of DiGeorge syndrome are also but less frequently observed in persons presenting with deletions in chromosome 4 8 10 17 or 18 with chromosomes 4 and 10 being the most frequently affected.
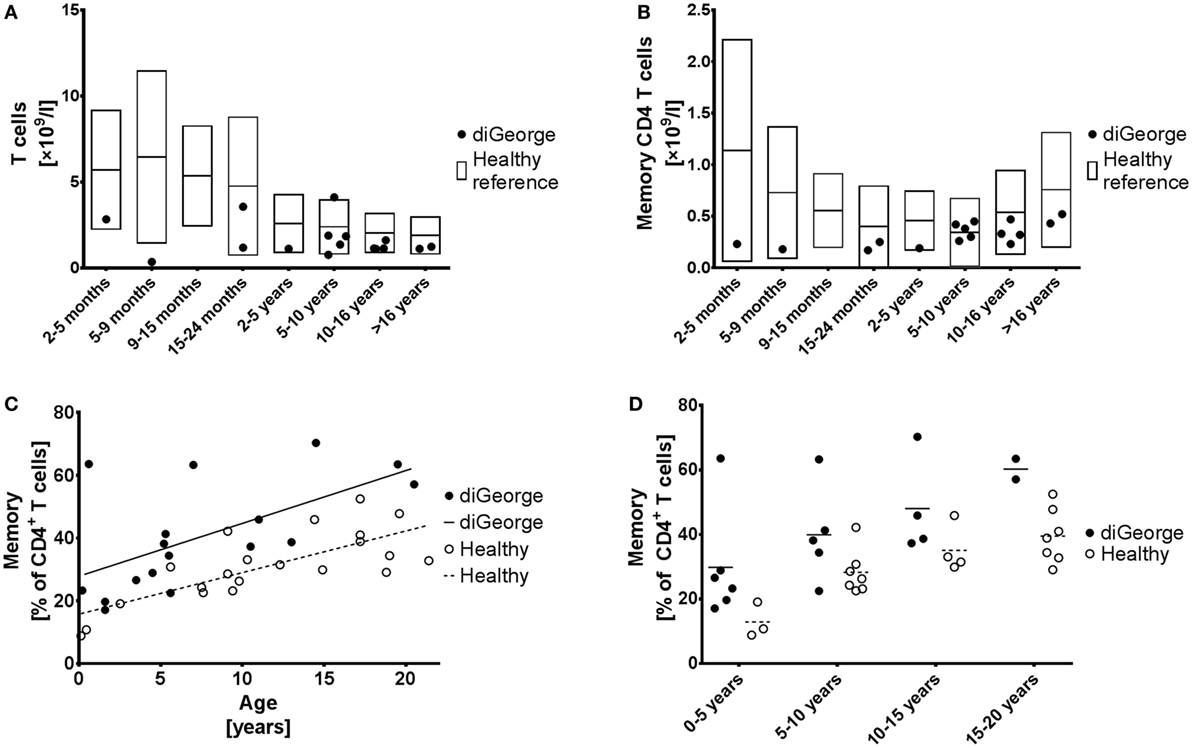
Symptoms and signs of DiGeorge often include. A 1-month mortality rate of 55 as well as a six-month mortality rate of 86 has been conveyed.
DiGeorge syndrome is associated with deletions or translocations of a small segment in the human chromosome 22.
DiGeorge syndrome also known as 22q112 deletion syndrome is a syndrome caused by the deletion of a small segment of chromosome 22. What is DiGeorge syndrome. In some cases DiGeorge syndrome 22q112 deletion syndrome may be passed from an affected parent to a child. Symptoms and signs of DiGeorge often include. 16p112 Deletion Syndrome. DiGeorge Syndrome Prognosis. DiGeorge syndrome also known as 22q112 deletion syndrome is a syndrome caused by the deletion of a small segment of chromosome 22. Most people with DiGeorge syndrome are missing a small piece of chromosome 22 known as. The most common disorder in which this occurs is DiGeorge syndrome caused by a deletion in the long or q arm of chromosome 22 leading to a hypoplasia of 3rd and 4th pharyngeal arches and their associated phayngeal pouches.
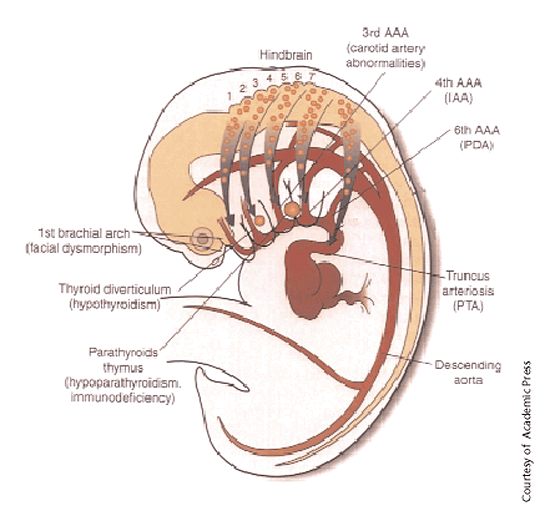
A 1-month mortality rate of 55 as well as a six-month mortality rate of 86 has been conveyed. In some cases DiGeorge syndrome 22q112 deletion syndrome may be passed from an affected parent to a child. Symptoms and signs of DiGeorge often include. This is the deletion of a segment of the short arm of the chromosome of about 25 genes affecting one of the pair of chromosome 16 in each cell. Some defects observed are linked to the pharyngeal pouch system which receives contribution from rostral migratory crest cells. The most common disorder in which this occurs is DiGeorge syndrome caused by a deletion in the long or q arm of chromosome 22 leading to a hypoplasia of 3rd and 4th pharyngeal arches and their associated phayngeal pouches. Ninety percent of cases of DiGeorge syndrome are caused by a segmental deletion in chromosome 22.






























Posting Komentar untuk "Which Cells Are Affected In Digeorge Syndrome?"