Vancomycin Red Man Syndrome
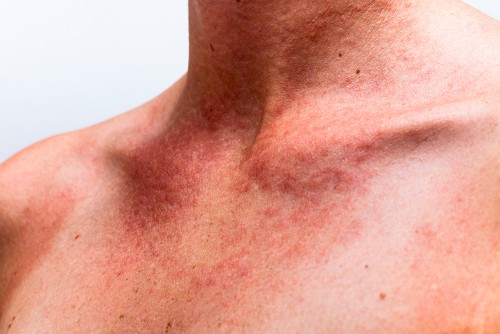
Vancomycin red man syndrome. Hypersensitivity reactions eg anaphylaxis red man syndrome Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders. Rapid infusion may cause red man syndrome see Adverse EffectsVancomycin levels are required to ensure that the target therapeutic range is achieved see Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. The most common symptom is the intense red rash that.
The terms red man syndrome or red neck syndrome have commonly been used to describe vancomycin flushing syndrome. Obtain culture prior to initiating therapy. The usual daily intravenous adult dose of Vancomycin is 2 g divided either as 500 mg every 6 hours or 1 g every 12 hours.
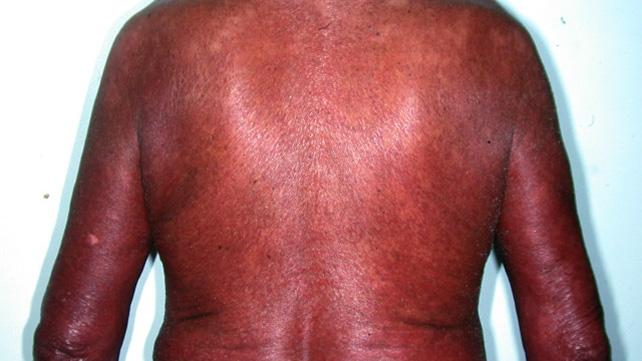
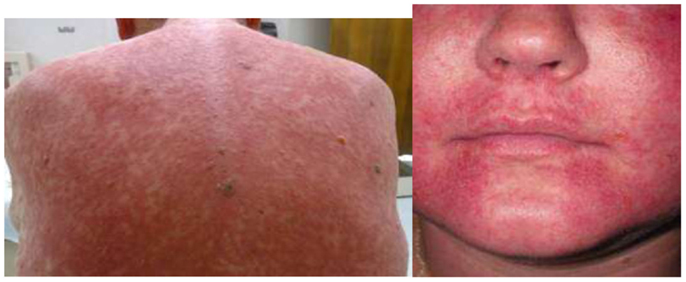
Symptoms include flushing of the upper body shortness of breath a skin rash itching pain muscle spasms and low blood pressure. Administer vancomycin intravenously IV over at least 1 hour. This terminology originated from the dramatic erythema that develops in some patients in response to infusion of vancomycin but the terms could be misconstrued as insulting to specific groups of people in the United States 1.
Dosage for Vancomycin Injection. Very rare less than 001. See also Antimicrobial guidelines.
Uncommon 01 to 1. Vancomycin is prescribed to treat serious bacterial infections including those of the bone blood and skin. Common 1 to 10.
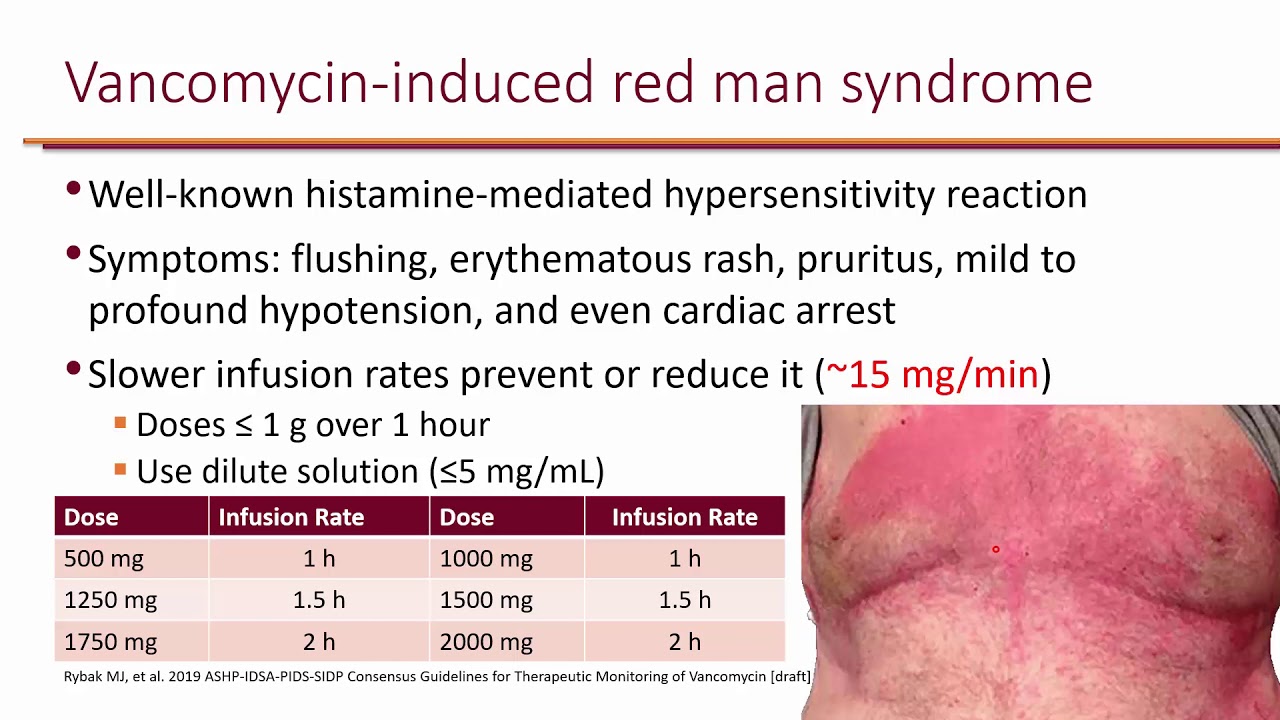
Red man syndrome most often occurs when vancomycin is infused too quickly but it can occur when the drug is given by other routes as well. Vancomycin is also associated with several forms of acute infusion reactions most notably anaphylaxis and the vancomycin flushing reaction previously known as red man syndrome. The next dose is timed to coincide with the falling concentration of the drug in the blood.
Treatment should include prolonging the infusion time to 3-4 hours. Continuous infusions of vancomycin in infants aged 0 to 90 days are associated.
See also Antimicrobial guidelines.
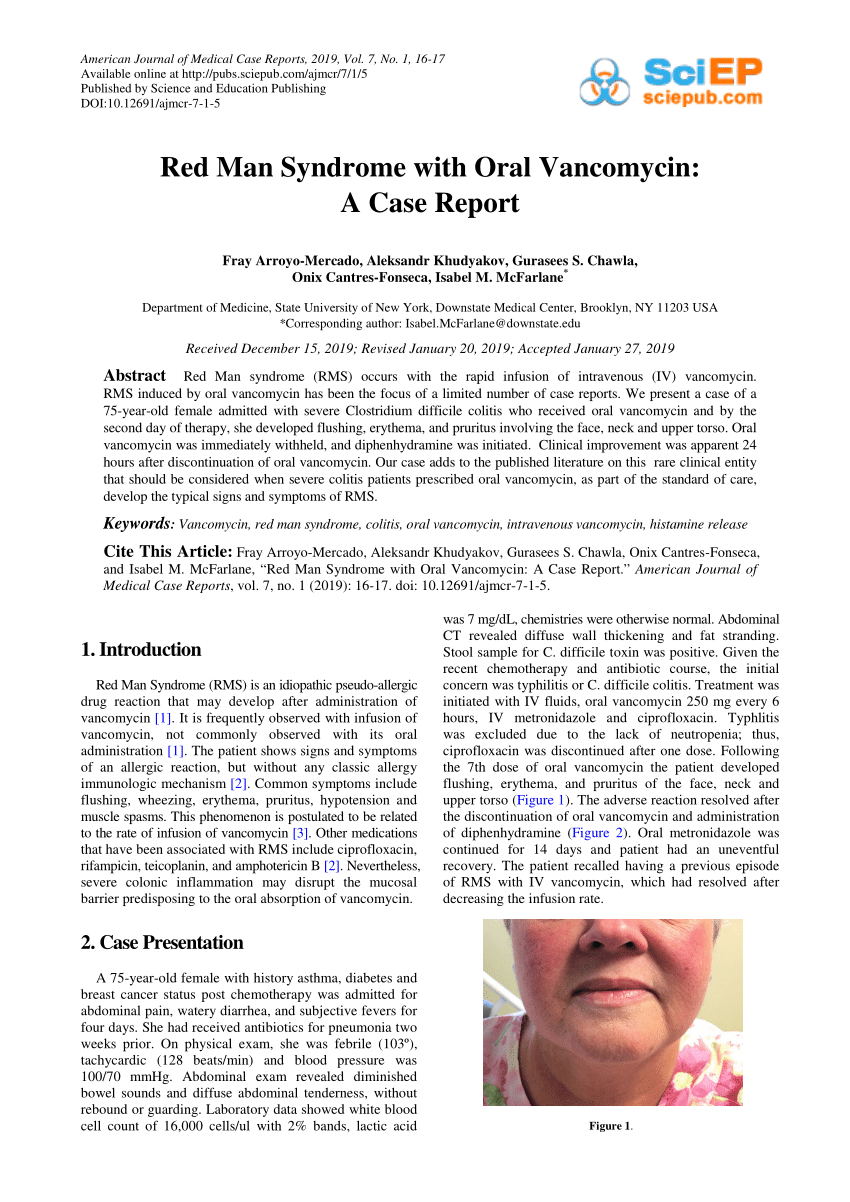
Severe dermatologic reactions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis. Red skin lesions often with a purple center red irritated eyes red swollen skin redness soreness or itching skin scaly skin sores welting or blisters sweating swelling of the feet or lower legs swollen glands unusual weight loss Other side effects not listed may also occur in some patients. Rarely Red Man Syndrome has been associated with vancomycin IV. Treatment should include prolonging the infusion time to 2-3 hours. However some may persist for several hours. This syndrome usually appearing within 4 to 10 min after the. Hypersensitivity reactions eg anaphylaxis red man syndrome Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders. Vancomycin flushing reactions occur typically during the first 15 to 20 minutes of an initial infusion of vancomycin most commonly when given rapidly and in. Vancomycin is also associated with several forms of acute infusion reactions most notably anaphylaxis and the vancomycin flushing reaction previously known as red man syndrome.
Red man syndrome is a response or hypersensitive reaction to the antibiotic vancomycin. Administer vancomycin intravenously IV over at least 1 hour. This test is used to monitor levels of the antimicrobial drug vancomycin in the blood. Common 1 to 10. To actions administer Vancomycin Hydrochloride for Injection in a diluted solution over a period of 60 minutes or greater and also prior to intravenous anesthetic agents. Vancomycin flushing reactions occur typically during the first 15 to 20 minutes of an initial infusion of vancomycin most commonly when given rapidly and in. Treatment should include prolonging the infusion time to 3-4 hours.




































Posting Komentar untuk "Vancomycin Red Man Syndrome"